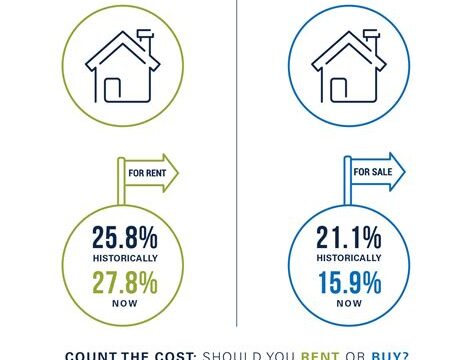
Understanding the costs of renting
To understand the costs of renting, it is important to consider all the different expenses that may come with renting a property. Renting, in many cases, may seem like a more affordable option compared to owning a home. However, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the associated costs to make an informed decision. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key costs involved in renting.
1. Monthly Rent: The most obvious cost when renting is the monthly rent payment. This is the amount you will need to pay each month to the landlord or property management company in order to keep your rental unit.
2. Security Deposit: Most landlords or property owners require tenants to pay a security deposit upfront. This deposit acts as a protection for the landlord in case of any damage to the property during the rental period. It is typically refundable, provided the property is left in good condition.
3. Utilities: Another cost to consider is the payment for utilities such as water, electricity, gas, and internet. Depending on the rental agreement, you may be responsible for paying these utility bills in addition to your monthly rent.
4. Renter’s Insurance: While not always mandatory, it is highly recommended to have renter’s insurance. This insurance provides coverage for your personal belongings in case of theft, damage, or other unforeseen circumstances. The cost of renter’s insurance will vary based on factors such as location, coverage amount, and insurance provider.
5. Maintenance and Repairs: Although the landlord is typically responsible for major repairs, tenants may be liable for certain maintenance costs. For example, if you accidentally damage something in the rental unit, you may be responsible for paying for repairs.
6. Moving Costs: Moving into a rental property often comes with its own set of costs. These may include hiring professional movers, renting a moving truck, or purchasing packing supplies. It’s important to budget for these expenses when considering the overall costs of renting.
7. Parking Fees: Depending on the location and type of rental property, you may have to pay extra for parking. This could be in the form of a monthly parking fee or an additional charge for a designated parking spot.
8. Pet Fees: If you have pets, some landlords may require an additional fee or a higher monthly rent to accommodate them. It’s important to clarify these costs before signing a rental agreement if you have furry friends.
9. Late Payment Fees: In case of late rent payments, landlords often charge late fees. These fees can vary and may accumulate over time, so it’s important to prioritize timely rent payments.
10. Moving Out Costs: Finally, when you decide to move out of a rental property, there may be costs associated with cleaning, repairing any damages you caused, or restoring the property to its original condition.
Considering all these costs will give you a better understanding of the financial implications of renting a property. It is important to carefully evaluate your budget and compare it with the rental costs to determine if renting is a viable option for you. Remember, it’s always a good idea to read and understand the terms of the rental agreement thoroughly before signing anything. Being well-informed about the costs involved in renting will help you make a more informed decision and ensure a smooth renting experience.
Evaluating the financial advantages of owning
Owning a home is a significant financial decision that comes with various advantages. Evaluating these advantages can help individuals make an informed choice when deciding between renting and owning. While renting provides flexibility and requires lower upfront costs, homeownership offers long-term financial stability and various financial benefits. In this blog post, we will delve into the financial advantages of owning a home and explore why it can be a wise investment.
1. Building Equity: One of the key financial advantages of owning a home is the opportunity to build equity. Equity is the difference between the market value of your home and the remaining mortgage balance. As you make mortgage payments, your equity gradually increases, building a valuable asset over time. Unlike renting, where your monthly payments only go towards the landlord’s profit, homeownership allows you to accumulate wealth through the appreciation of the property.
2. Tax Benefits: Another noteworthy advantage of owning a home are the tax benefits that come with it. Homeowners can deduct mortgage interest, property taxes, and certain loan origination fees from their annual tax returns. These deductions can significantly reduce the overall tax liability, providing homeowners with additional savings. Moreover, if you sell your primary residence after living in it for at least two years, you may qualify for a capital gains tax exemption up to a certain limit.
3. Potential for Appreciation: Real estate has historically appreciated in value over time, making it a potentially lucrative investment. Although market conditions can vary, homeowners generally benefit from the appreciation of their property’s value in the long run. This appreciation allows homeowners to build wealth and potentially sell their property for a higher price in the future. Additionally, homeowners can leverage their property’s increased value to access additional financing options, such as home equity loans or lines of credit.
- Owning a home offers the potential for long-term financial stability.
- Tax benefits, such as deductions and exemptions, can provide homeowners with significant savings.
- Real estate has the potential to appreciate, allowing homeowners to build wealth over time.
| Financial Advantages of Owning | Summary |
|---|---|
| Building Equity | As mortgage payments are made, homeowners build equity and accumulate a valuable asset. |
| Tax Benefits | Homeowners can deduct mortgage interest, property taxes, and certain loan fees from their tax returns. |
| Potential for Appreciation | Real estate has historically appreciated in value, allowing homeowners to potentially sell for a higher price in the future. |
Considering the financial advantages described above, it becomes evident that owning a home can be a financially wise decision in the long run. While it may require a larger upfront investment and greater responsibility for maintenance, homeownership offers the potential for wealth accumulation and stability. By carefully evaluating personal financial circumstances and future goals, individuals can make an informed decision about whether owning a home is the right choice for them.
Comparing monthly expenses: renting vs. owning
When it comes to comparing monthly expenses, both renting and owning a home have their own set of financial implications. It is important to evaluate and weigh the costs associated with each option to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle choices.
List of Monthly Expenses:
– Rent: When renting a home, the primary monthly expense is the rent amount that you pay to the landlord or property management company. The rent can vary depending on the location, size, and condition of the rental property.
– Mortgage Payment: Alternatively, when you own a home, your primary monthly expense would be the mortgage payment. This payment includes both the principal amount and the interest charged on the loan.
– Property Taxes: Homeowners are often responsible for paying property taxes, which are based on the assessed value of the property.
– Homeowners Insurance: Owning a home typically requires you to have homeowners insurance to protect your property from damages and liabilities.
– Utilities: Both renters and homeowners have to consider monthly utility costs, which include electricity, water, gas, internet, and other utility services.
– Maintenance and Repairs: Renters typically have less responsibility when it comes to maintenance and repairs as they are usually handled by the landlord. However, homeowners need to account for the costs associated with maintaining and repairing their property.
Table Comparing Monthly Expenses:
| Expense | Renting | Owning |
|---|---|---|
| Rent/Mortgage Payment | Varying monthly rent amount | Fixed mortgage payment |
| Property Taxes | N/A | Based on property value |
| Homeowners Insurance | N/A | Required |
| Utilities | Typically paid separately | Typically paid separately |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Usually handled by landlord | Responsibility of the homeowner |
It is crucial to analyze your current financial situation and priorities before making a decision. Renting may provide more flexibility in terms of short-term commitments and fewer financial responsibilities, while owning a home offers the potential for building equity and stability in the long run. As everyone’s circumstances differ, considering the financial aspects along with emotional and lifestyle factors can help you determine which option is more suitable for you.
Analyzing long-term financial implications
When it comes to making big financial decisions, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications. This is especially true when it comes to the choice between renting and owning a property. While renting may seem like the easier and more affordable option in the short term, it is essential to understand the potential financial impact over the long run.
One of the key factors to consider when analyzing the long-term financial implications is building equity through ownership. With homeownership, monthly mortgage payments help to build equity in the property. This means that over time, as you pay down your mortgage and the value of your home increases, you are building wealth. Renting, on the other hand, does not offer this opportunity to accumulate equity.
Another crucial aspect to analyze long-term is the investment potential of owning a property. Real estate has historically been considered a solid investment, with property values generally appreciating over time. By owning a home, you have the potential to benefit from this increase in value. This can be particularly advantageous if you plan to stay in the property for many years, as it allows you to leverage your investment and potentially generate a substantial return.
| Costs | Renting | Owning |
|---|---|---|
| Mortgage Payments | – | + |
| Property Taxes | – | + |
| Insurance | – | + |
| Maintenance and Repairs | – | + |
| Potential Appreciation | – | + |
Comparing the monthly expenses of renting versus owning is also essential in analyzing the long-term financial implications. While renting may have lower monthly expenses in terms of mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and maintenance costs are typically the responsibility of the landlord. However, as a homeowner, you will have to take on these expenses yourself. It is vital to evaluate your budget and determine whether you can comfortably afford these additional costs.
Lastly, it is crucial to weigh the emotional and lifestyle aspects when analyzing the long-term financial implications. Renting offers flexibility and the ability to relocate more easily. On the other hand, owning a home provides stability and the opportunity to build roots in a community. It is important to consider your personal preferences and long-term goals.
In conclusion, when analyzing the long-term financial implications of renting versus owning a property, it is important to consider factors such as building equity, investment potential, monthly expenses, and lifestyle aspects. Owning a home can offer the opportunity to build equity, benefit from potential appreciation, and provide stability. However, it is essential to also consider the additional costs and responsibilities associated with homeownership. Ultimately, it is crucial to make a decision that aligns with your financial goals and lifestyle.
Considering the flexibility of renting
When it comes to housing options, one of the main decisions you will have to make is whether to rent or to own a property. Both choices have their own set of pros and cons, and it’s crucial to carefully consider each aspect before making a decision. In this blog post, we will focus on the flexibility of renting and why it can be an attractive option for many individuals.
1. Temporary Living Arrangement: One significant advantage of renting is the flexibility it offers in terms of your living arrangements. Renting allows you the freedom to move easily, especially if you are unsure about your long-term plans or if your job requires frequent relocations. You can change neighborhoods, cities, or even countries without worrying about the complicated process of selling a property.
2. Less Financial Commitment: Renting often requires a smaller financial commitment compared to owning a home. While there may be a security deposit and monthly rent payments, you are not responsible for property taxes, homeowners insurance, or major repairs. This can provide you with more disposable income, allowing you to pursue other financial goals or enjoy a higher quality of life.
3. Access to Amenities: Another advantage of renting is the potential access to amenities that may be cost-prohibitive in home ownership. Many rental properties come with various amenities such as pools, fitness centers, or communal spaces that may be included in your rent. This can provide you with a convenient and hassle-free lifestyle where you can enjoy these amenities without the additional expenses and effort of maintaining them.
All in all, renting offers a significant level of flexibility that can suit various lifestyles and circumstances. It provides the opportunity to live in different locations, requires less financial commitment, and often grants access to desirable amenities. However, it’s essential to weigh these advantages against the potential disadvantages, such as limited control over the property and the possibility of rent increases. Ultimately, the decision between renting and owning depends on your personal preferences, financial situation, and long-term goals.
Investment potential: building equity through ownership
One of the major advantages of owning a home is the potential to build equity. Equity is the value of a property that is not owed to the mortgage lender. As homeowners make mortgage payments, their equity in the property increases. This is in contrast to renting, where monthly payments only provide temporary accommodation without any long-term financial gain. By gradually paying off their mortgage, homeowners can build equity and ultimately increase their personal wealth.
Building equity through ownership offers numerous financial benefits. Firstly, it allows homeowners to accumulate wealth over time. As the equity in their property grows, homeowners have the potential to sell the property for a profit. This profit can then be used to purchase a larger or more desirable home, invest in other real estate ventures, or simply provide financial security for the future.
Additionally, building equity can also provide homeowners with access to extra funds through home equity loans or lines of credit. These financial products allow homeowners to tap into the accumulated equity in their homes and use it for various purposes, such as home improvements, education expenses, or debt consolidation. The availability of such funds can be a significant advantage, as it offers homeowners a source of low-interest financing to support their financial goals.
- Builds personal wealth over time
- Potential to sell property for profit
- Access to home equity loans or lines of credit
- Provides low-interest financing options
| Advantages of Building Equity | Disadvantages of Building Equity |
|---|---|
| Increased personal wealth | Property value fluctuations |
| Potential for profit upon selling | Requires relatively long-term commitment |
| Access to additional funds through home equity | Risk of foreclosure if mortgage payments are not met |
In conclusion, owning a home comes with the advantage of building equity. This offers homeowners the opportunity to accumulate wealth, potentially make a profit upon selling, and access additional funds through home equity products. However, it is important to consider the potential disadvantages, such as property value fluctuations and the long-term commitment required. Overall, building equity through homeownership can be a key factor in securing a stable and prosperous financial future.
Factoring in maintenance and repair costs
Factoring in maintenance and repair costs is an important aspect to consider when deciding between renting and owning a property. While renting can provide a sense of freedom from these responsibilities, it is essential to understand the potential financial implications associated with maintenance and repairs as a homeowner.
As a homeowner, you have the sole responsibility for maintaining and repairing your property. This means that any unexpected repairs or regular maintenance tasks must be funded by you. From fixing leaky faucets to replacing damaged roofs, these costs can quickly add up. It is crucial to budget for these expenses and set aside funds to cover any unforeseen repairs that may arise.
One advantage of renting is that maintenance and repair costs are typically the responsibility of the landlord or property management company. This provides tenants with a sense of convenience and financial security, as any necessary repairs are taken care of by someone else. However, it is important to note that landlords may choose to increase rent to cover these expenses, so it’s essential to evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness of renting in the long run.
Another factor to consider is the age and condition of the property. Older homes or properties in need of renovation may require more frequent and costly repairs. On the other hand, newly constructed or recently renovated properties may have fewer maintenance issues initially. It is vital to assess the condition of the property before making a decision and factor in potential repair costs based on its current state.
Creating a comprehensive list of possible maintenance and repair expenses can help in estimating the overall cost of homeownership. This list can include various items such as HVAC system repairs, plumbing issues, electrical problems, pest control, and general upkeep. By conducting thorough research and seeking advice from professionals, you can gain a better understanding of the potential costs involved.
In conclusion, it is essential to factor in maintenance and repair costs when considering the financial implications of renting versus owning. While renting may provide convenience and relief from these responsibilities, owning a property comes with the potential for unexpected repair expenses. By budgeting for maintenance costs and thoroughly assessing the condition of a property, individuals can make an informed decision that aligns with their financial goals and circumstances.
Weighing the emotional and lifestyle aspects
When it comes to making a decision between renting and owning a home, people often focus solely on the financial aspects. However, it’s important to also consider the emotional and lifestyle aspects before making such a big decision. These factors can greatly impact your overall happiness and satisfaction with your living situation.
One of the advantages of renting is the flexibility it offers. Renting allows you to easily change your living situation if you need to relocate for work or other reasons. You’re not tied down to a particular property and can explore different neighborhoods or cities without the commitment of owning a home. This flexibility can be especially beneficial for young professionals or those who prefer a nomadic lifestyle.
On the other hand, owning a home provides a sense of stability and security. Homeownership often comes with a deeper connection to the community and a feeling of belonging. You have the freedom to personalize and make changes to your home without worrying about landlord restrictions. Many homeowners also take pride in ownership and enjoy the sense of accomplishment that comes with investing in their own property.
- Financial Stability: While renting may offer more flexibility, owning a home can provide long-term financial stability. As you continue to make mortgage payments, you’re building equity and gradually owning a valuable asset. In the long run, owning a home can be a more stable investment compared to renting, where your money goes towards someone else’s property.
- Maintenance and Responsibilities: One aspect of homeownership that needs to be considered is the responsibility for maintenance and repairs. As a homeowner, you’re responsible for taking care of any repairs or maintenance needed for your property. This can be both time-consuming and expensive. On the other hand, as a renter, these responsibilities typically fall on the landlord, allowing you to have a more carefree living experience.
- Emotional Well-being: The emotional aspect of homeownership should not be overlooked. Owning a home can bring a sense of pride, stability, and a feeling of belonging to a community. It allows you to create roots and build long-lasting relationships with neighbors. On the other hand, renting offers the freedom to easily move and explore different living situations, which can be appealing to those who crave variety and change.
At the end of the day, the decision between renting and owning is a personal one that depends on your own priorities and values. Understanding the emotional and lifestyle aspects, in addition to the financial considerations, is crucial in making an informed decision. Whether you choose to rent or own, it’s important to listen to your intuition and choose the option that aligns with your goals and aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the costs associated with renting a property?
The costs of renting typically include monthly rent payments, security deposits, application fees, and possibly additional fees for utilities or parking.
2. How do the financial advantages of owning a home compare to renting?
Owning a home can provide financial advantages, such as potential tax deductions, building equity, and the opportunity for appreciation, whereas renting does not offer these benefits.
3. How do monthly expenses differ for renting versus owning?
Renting generally includes fixed monthly rent payments, while owning a home may involve mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and possibly homeowner association fees.
4. What are the long-term financial implications of owning versus renting?
Owning a home can offer long-term financial stability and the potential to build wealth through equity, while renting may lack the opportunity for long-term financial growth or stability.
5. What are the advantages of renting in terms of flexibility?
Renting provides the flexibility to easily move to a new location or downsize, without the responsibilities and costs associated with selling a home.
6. How does owning a home contribute to investment potential and building equity?
By making mortgage payments, homeowners gradually build equity in their property, which can serve as an investment and potentially be leveraged for future financial goals.
7. How do maintenance and repair costs factor into the decision to rent or own?
When renting, maintenance and repair costs are typically the responsibility of the landlord, whereas homeowners are responsible for these costs when owning a property.
8. What emotional and lifestyle aspects should be considered when deciding between renting and owning?
Factors such as the desire for stability, the freedom to personalize a living space, and the sense of pride in homeownership are emotional and lifestyle considerations that can impact the decision to rent or own.