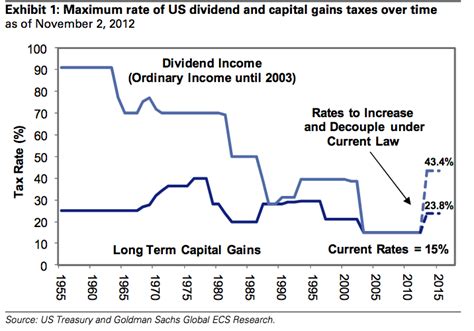
Understanding Dividend and Capital Gain Income
When it comes to investing, it’s important to understand the different types of income that can be generated. Two common forms of income for investors are dividend income and capital gain income. These types of income can have different tax implications, so it’s essential to have a clear understanding of how they work and how they can impact your overall investment strategy.
Dividend income is the money that an investor receives from owning shares of stock in a company that distributes a portion of its profits to shareholders. These distributions are typically paid on a regular basis, such as quarterly or annually. Dividend income can be a valuable source of consistent income for investors, especially those who are looking for income in addition to potential capital appreciation.
Capital gain income, on the other hand, is the profit that an investor earns when they sell an investment for a higher price than what they originally paid for it. This can occur with various types of investments, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and more. Capital gains can be either short-term or long-term, depending on how long the investment was held before being sold.
The Importance of Tax Planning for Investors
When it comes to managing your investment income, tax planning plays a crucial role. The decisions you make regarding the timing of buying and selling investments, as well as the types of investments you choose, can have a significant impact on your tax liability.
One effective tax planning strategy for dividend income is to invest in tax-advantaged accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. By doing so, you can potentially defer taxes on the dividends received until you begin withdrawing funds from the account in retirement.
Additionally, it’s important to consider the tax implications of capital gains when planning your investment strategy. If you have investments that have appreciated significantly in value, you may want to hold onto them for at least one year to qualify for the more favorable long-term capital gains tax rates. However, if you have investments that have depreciated in value, you may want to consider selling them to realize capital losses that can be used to offset any capital gains you may have.
Maximizing Tax Efficiency in Dividend Income
To maximize the tax efficiency of your dividend income, you can also consider the option of reinvesting your dividends. By reinvesting your dividends back into the same investment or purchasing additional shares, you can potentially increase your overall return over time. This can be particularly beneficial if you have a long-term investment horizon.
Another strategy for maximizing tax efficiency in dividend income is to invest in dividend stocks that qualify for the qualified dividend tax rate. Qualified dividends are taxed at the same rates as long-term capital gains, which can be lower than ordinary income tax rates. However, not all dividend stocks qualify for this preferential tax treatment, so it’s important to do your research before making any investment decisions.
Utilizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts for Investments
In addition to using tax-advantaged accounts to defer taxes on dividend income, they can also be used to defer taxes on capital gains. By holding investments in tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k) plans, you can potentially defer taxes on any capital gains until you begin taking withdrawals from the account. This can be advantageous, especially if you have investments that have a high likelihood of appreciating in value over time.
Furthermore, tax-advantaged accounts can also provide additional benefits, such as potential tax deductions for contributions and the ability to grow investments on a tax-deferred basis. These advantages can help investors maximize their overall returns and minimize their tax liability.
Minimizing Tax Liability through Dividend Reinvestment
In addition to the tax efficiency benefits mentioned earlier, reinvesting your dividends can also help minimize your overall tax liability. By reinvesting your dividends rather than taking them as cash, you can potentially avoid paying taxes on the dividend income in the current year. Instead, the reinvested dividends will be added to your cost basis in the investment, which can help reduce any potential capital gains taxes when you ultimately sell the investment.
It’s important to note that while tax planning is an important aspect of investing, it should not be the sole driving factor in making investment decisions. It’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified financial advisor or tax professional to ensure that your investment strategy aligns with your financial goals and overall tax situation.
Importance of Tax Planning for Investors
Investing can be a rewarding experience, both financially and personally. As an investor, it’s important to understand the various aspects of investment, including taxation. Tax planning is a crucial part of investment strategy that often goes overlooked by many investors. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of tax planning for investors and how it can help maximize your returns.
One of the key reasons why tax planning is essential for investors is that it allows you to minimize your tax liability. By taking advantage of tax deductions, credits, and other incentives, you can legally reduce the amount of tax you owe. This can result in significant savings over time, allowing you to keep more of your investment returns.
Another benefit of tax planning is that it enables you to maximize your after-tax returns. When you proactively consider the tax implications of your investment decisions, you can structure your portfolio in a way that optimizes your after-tax returns. By minimizing the impact of taxes on your investments, you can potentially earn higher overall returns in the long run.
Furthermore, tax planning can also help you manage your cash flow effectively. By understanding the timing of your tax obligations and implementing strategies such as tax loss harvesting or capital gain offsetting, you can ensure that you have sufficient cash on hand to meet your tax obligations without disrupting your investment plans.
- Tax deductions: Expenses incurred for investment-related activities, such as advisory fees or research expenses, may be deductible.
- Tax credits: Certain investments, such as renewable energy or low-income housing, may qualify for tax credits.
- Tax-advantaged accounts: Utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s can provide you with potential tax benefits.
By leveraging these tax planning strategies, you can effectively minimize your tax liability and maximize your returns as an investor. It’s vital to stay informed about the current tax laws and consult with a tax professional to ensure you are taking full advantage of any available tax-saving opportunities.
Maximizing Tax Efficiency in Dividend Income
When it comes to investing, one of the key considerations for investors is the tax implications of their income. Maximizing tax efficiency in dividend income is a strategy that can help investors reduce their tax liability and maximize their overall returns. By understanding the tax rules and regulations surrounding dividend income, investors can make informed decisions and optimize their investment strategy.
Dividend income refers to the payments that investors receive from companies in which they hold shares. These payments are typically a portion of the company’s profits, distributed to shareholders as a way to reward their investment. Dividend income can be a valuable source of income for investors, providing regular cash flow and potential growth.
Tax planning plays a crucial role in maximizing the tax efficiency of dividend income. By strategically planning and managing their investments, investors can minimize the amount of tax they owe on their dividends. One effective strategy is to hold dividend-paying stocks in tax-advantaged accounts such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. These accounts offer tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals, allowing investors to grow their dividend income without incurring significant tax liabilities.
Listed below are some key points to consider for maximizing tax efficiency in dividend income:
- Utilize tax-advantaged accounts: Investing in tax-advantaged accounts can provide significant tax benefits, allowing investors to maximize their dividend income. Contributions to these accounts may be tax-deductible, and withdrawals are often taxed at a lower rate or even tax-free.
- Reinvest dividends: By reinvesting dividends back into the investment, investors can potentially benefit from compounding returns. This strategy can help to grow the investment over time and defer the tax liability on the dividends until a later date.
- Consider tax rates: Understanding the different tax rates that apply to dividend income is crucial for tax planning. Depending on the holding period and the investor’s tax bracket, dividends may be subject to different tax rates, ranging from ordinary income tax rates to preferential tax rates.
Table: Tax Rates for Dividend Income
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate on Dividends |
|---|---|
| 10% or 15% | 0% |
| 25% or higher | 15% |
| 39.6% | 20% |
By carefully considering these strategies and utilizing the available tax benefits, investors can maximize their tax efficiency in dividend income. It is important for investors to consult with a qualified tax advisor or financial professional to tailor these strategies to their individual circumstances and ensure compliance with tax laws.
Effective Strategies for Capital Gain Tax Planning
When it comes to tax planning, it is important for investors to understand the various strategies available to them. One area that often requires careful consideration is capital gains tax. Capital gains are the profits that an individual or entity makes from the sale of a capital asset, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. These gains are subject to taxation, but there are strategies that investors can employ to minimize their tax liability.
One effective strategy for capital gain tax planning is to hold onto assets for longer periods of time. This is known as long-term investing. By holding onto investments for more than one year, investors can qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates, which are typically lower than short-term rates. This can result in significant tax savings, especially for individuals in higher income brackets.
Another strategy for capital gain tax planning is to offset capital losses with capital gains. When investors sell assets at a loss, they can use those losses to offset the capital gains realized from the sale of other assets. This can help to reduce the overall tax liability. It is important to note, however, that there are specific rules and limitations surrounding the use of capital losses for tax purposes.
- Long-term investing
- Offsetting capital losses with capital gains
- Maximizing tax efficiency
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Long-term investing | Holding onto assets for more than one year to qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates. |
| Offsetting capital losses with capital gains | Using capital losses to reduce the overall tax liability by offsetting them against capital gains. |
| Maximizing tax efficiency | Employing various strategies and tactics to minimize tax liability on capital gains. |
One additional strategy for capital gain tax planning is to maximize tax efficiency. This involves leveraging various tax-advantaged accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s, to invest in assets that generate capital gains. By utilizing these accounts, investors can enjoy tax advantages such as tax-free growth or tax deferral.
In conclusion, effective capital gain tax planning involves implementing strategies such as long-term investing, offsetting capital losses with capital gains, and maximizing tax efficiency. By carefully considering these strategies, investors can minimize their tax liability and maximize their after-tax returns. It is important to consult with a qualified tax professional to ensure that these strategies are implemented correctly and in accordance with relevant tax laws and regulations.
Utilizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts for Investments
When it comes to investing, it is important to consider all available strategies to optimize your returns. One such strategy is to take advantage of tax-advantaged accounts. These accounts can provide significant tax benefits and help you maximize your investment growth. Let’s explore the different types of tax-advantaged accounts and how they can benefit investors.
One of the most popular tax-advantaged accounts is the Individual Retirement Account (IRA). IRAs come in two main types: Traditional and Roth. With a Traditional IRA, contributions are typically tax-deductible, and the earnings grow tax-deferred until you make withdrawals during retirement. On the other hand, Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars, allowing for tax-free withdrawals in retirement. Both options provide investors with the opportunity to grow their investments without the burden of immediate taxation.
Another tax-advantaged account worth exploring is the Health Savings Account (HSA). Designed specifically for medical expenses, an HSA allows you to contribute pre-tax income to the account, grow those funds tax-free, and make tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. HSAs offer a triple tax advantage, making them an attractive option for individuals looking to save for healthcare costs while reducing their tax burden.
| Type of Tax-Advantaged Account | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Individual Retirement Account (IRA) |
|
| Health Savings Account (HSA) |
|
Lastly, 529 plans are another tax-advantaged account that can be utilized for educational expenses. These plans allow individuals to save for future education costs for either themselves or their loved ones. Contributions to a 529 plan grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals for educational expenses are also tax-free. This makes 529 plans a valuable tool for individuals looking to invest in their or their children’s education while minimizing their tax liability.
In conclusion, utilizing tax-advantaged accounts can significantly enhance your investment strategy. Whether it’s an IRA, HSA, or a 529 plan, these accounts offer various tax benefits that can help maximize your investment growth. By taking advantage of these accounts, investors can reduce their tax liability and ultimately increase their overall returns. So, consider incorporating tax-advantaged accounts into your investment plan and make the most of the tax benefits they offer.
Offsetting Capital Losses with Capital Gains
Capital losses and capital gains are two terms frequently used in the world of investing and taxation. Understanding how these concepts work is crucial for investors looking to minimize their tax liability and maximize their overall financial gains.
When an investor sells an asset for a price lower than its purchase price, they incur a capital loss. Conversely, when an investor sells an asset for a price higher than its purchase price, they earn a capital gain. Both losses and gains can have significant implications for taxation.
One crucial strategy for minimizing tax liability is offsetting capital losses with capital gains. This strategy involves using the losses incurred on certain investments to reduce the taxes owed on the gains earned through other investments.
List of strategies for offsetting capital losses with capital gains:
- Harvesting losses: Investors can intentionally sell investments that have experienced losses to offset any capital gains made during the same year. By doing so, they can effectively reduce their overall taxable income.
- Capital loss carryforward: If an investor has more capital losses than capital gains in a given year, they can carry forward the unused losses to offset future gains. This strategy allows them to reduce their tax liability over multiple years.
- Be mindful of wash sales: The IRS has specific rules regarding the sale and repurchase of the same or substantially identical investment within a short period of time (typically 30 days). Investors must be cautious of wash sales, as they can disallow the offset of capital losses for tax purposes.
A table demonstrating the tax implications of offsetting capital losses with capital gains:
| Scenario | Capital Losses | Capital Gains | Taxable Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| No offsetting | $0 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Offsetting losses | $5,000 | $10,000 | $5,000 |
| Offsetting losses and carryforward | $9,000 | $10,000 | $1,000 |
As illustrated in the table above, offsetting capital losses with capital gains can significantly reduce taxable income. This can lead to substantial tax savings for investors and allow them to keep more of their investment earnings.
It is important for investors to consult with a qualified tax professional or financial advisor to determine the specific strategies and tax implications that best suit their individual circumstances. Each investor’s financial situation may vary, and personalized tax planning is essential for maximizing tax efficiency and minimizing tax liability.
Minimizing Tax Liability through Dividend Reinvestment
Understanding Dividend and Capital Gain Income
When it comes to investing, one of the key considerations for investors is minimizing their tax liability. One effective strategy to achieve this goal is through dividend reinvestment. By reinvesting dividends, investors can potentially reduce their tax obligations while maximizing their returns.
Dividend reinvestment is the process of using the dividends received from a company to purchase additional shares of the same company’s stock. Instead of receiving the dividends in cash, investors choose to reinvest them back into the investment. This strategy allows investors to take advantage of compound growth over time and potentially increase their overall investment value.
One of the major benefits of dividend reinvestment is its tax advantages. When dividends are reinvested, they are not considered as taxable income in the year they are received. This means that investors can defer paying taxes on their dividends until they sell the shares in the future. By deferring taxes, investors can potentially benefit from compounding returns and delay their tax liability.
- Tax Efficiency: Dividend reinvestment allows investors to defer taxes on their dividends, leading to potentially higher overall returns.
- Compound Growth: By reinvesting dividends, investors can take advantage of compound growth, potentially increasing the value of their investments over time.
- Long-Term Strategy: Dividend reinvestment is particularly beneficial for long-term investors who are focused on building wealth and minimizing tax obligations.
In addition to the tax advantages, dividend reinvestment also offers convenience for investors. Instead of manually reinvesting dividends, many brokerage firms provide automatic dividend reinvestment programs. This allows investors to reinvest their dividends without having to take any additional actions. It simplifies the process and ensures that dividends are automatically reinvested in a timely manner.
It is important to note that while dividend reinvestment can be a beneficial strategy for minimizing tax liability, investors should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to fully understand the implications and potential tax savings specific to their individual circumstances. Tax laws and regulations may vary, and it is essential to make informed decisions based on one’s personal financial situation.
| Benefits of Dividend Reinvestment | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Tax efficiency | Consult with a financial advisor |
| Compound growth potential | Understand individual tax laws |
| Convenience for investors | Make informed decisions |
Long-Term Investing and Tax Planning for Investors
When it comes to investing, one of the key considerations for investors is tax planning. While maximizing returns is important, minimizing tax liability can significantly impact the overall profitability of an investment portfolio. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of long-term investing and tax planning for investors, and how these two strategies can work together to create a more tax-efficient investment strategy.
Long-term investing is a strategy that focuses on holding investments for an extended period, typically five years or more. This approach allows investors to benefit from the power of compounding and ride out short-term market fluctuations. It also offers several tax advantages compared to short-term investing. For example, long-term capital gains are typically taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains, providing an opportunity for investors to reduce their tax liability.
One effective strategy for long-term investing and tax planning is to utilize tax-advantaged accounts such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s. These accounts offer tax advantages, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals in retirement. By contributing to these accounts, investors can potentially lower their taxable income in the current year while also building a tax-advantaged nest egg for the future.
- Contributions to traditional IRAs may be tax-deductible, providing an immediate tax benefit.
- Roth IRAs offer tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement, making them an attractive option for long-term investors.
- 401(k) plans, especially those with employer matching contributions, can provide a significant boost to an investor’s retirement savings.
Another aspect of long-term investing and tax planning is the reinvestment of dividends. Many companies offer dividend payment as a way to distribute profits to shareholders. Rather than taking these dividends as cash, investors can choose to reinvest them back into the investment. By doing so, investors can potentially benefit from the power of compounding and defer taxes on these reinvested dividends until they are eventually sold.
In summary, long-term investing and tax planning go hand in hand for investors. By taking a long-term approach, investors can benefit from lower tax rates on capital gains, while also utilizing tax-advantaged accounts to further reduce their taxable income. By reinvesting dividends, investors can also defer taxes and potentially supercharge the growth of their investments. As with any investment strategy, it is important for investors to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure their tax planning aligns with their long-term investment goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is the importance of tax planning for investors?
Tax planning is important for investors because it helps them minimize their tax liability and maximize their after-tax returns. By strategically managing their investments and taking advantage of available tax deductions, credits, and exemptions, investors can reduce the amount of taxes they owe and keep more of their earnings.
Question 2: How can investors maximize tax efficiency in dividend income?
Investors can maximize tax efficiency in dividend income by holding dividend-paying stocks in tax-advantaged accounts like Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. This allows them to defer taxes on their dividends until they withdraw the funds in retirement when they may be in a lower tax bracket.
Question 3: What are effective strategies for capital gain tax planning?
Effective strategies for capital gain tax planning include holding investments for longer periods to qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates, utilizing tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains with capital losses, and considering tax-efficient investment vehicles like index funds or ETFs that have lower turnover and minimize capital gain distributions.
Question 4: How can investors utilize tax-advantaged accounts for investments?
Investors can utilize tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs, 401(k) plans, or Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to shelter their investments from immediate taxation. Contributions to these accounts may be tax-deductible or grow tax-free, allowing investors to accumulate wealth and reduce their taxable income.
Question 5: How can investors offset capital losses with capital gains?
Investors can offset capital losses with capital gains by engaging in tax-loss harvesting. This involves selling investments that have declined in value to realize the losses, which can then be used to offset the taxable gains from other investments. This strategy helps reduce overall tax liability.
Question 6: How can investors minimize tax liability through dividend reinvestment?
Investors can minimize tax liability through dividend reinvestment by automatically reinvesting their dividends to purchase additional shares of the same investment. This allows investors to defer paying taxes on the distributed dividends until they eventually sell the shares, potentially at a more tax-favorable time or when they are in a lower tax bracket.
Question 7: How does long-term investing relate to tax planning for investors?
Long-term investing is closely related to tax planning for investors because holding investments for longer periods can qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates. By strategically aligning their investment goals with long-term investment horizons, investors can maximize after-tax returns and minimize their tax burden.