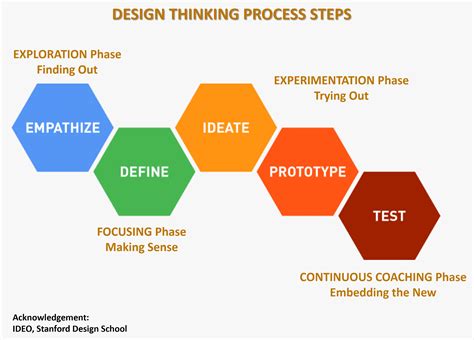
Understanding design thinking principles
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing world, design thinking has emerged as a powerful methodology to solve complex problems and drive innovation. Design thinking is not limited to designers; it can be applied by individuals from various disciplines who are looking to create impactful solutions. To truly understand and apply design thinking principles, let’s delve deeper into its core concepts and explore how it can be used to unleash creativity and foster innovation.
1. Human-Centered Approach:
Design thinking revolves around a human-centered approach, placing people at the heart of the problem-solving process. It emphasizes understanding the needs, desires, and challenges of the end-users or customers. By empathizing with users, designers gain valuable insights into their experiences and can develop solutions that truly address their needs.
2. Iterative and Collaborative Process:
A key aspect of design thinking is its iterative nature. Rather than following a linear path, the design process involves repeated cycles of ideation, prototyping, testing, and refining. This enables designers to continuously learn, adapt, and improve their solutions based on feedback and real-world observations. Collaboration plays a crucial role in this process, as it encourages diverse perspectives and collective problem-solving.
3. Embracing Ambiguity and Experimentation:
Design thinking embraces ambiguity and encourages designers to explore multiple possibilities. It encourages them to think outside the box, challenge assumptions, and take risks. This mindset fosters a culture of experimentation, where failure is seen as an opportunity for learning and growth. By embracing ambiguity and encouraging experimentation, design thinking opens up new avenues for innovative solutions.
By understanding these fundamental principles of design thinking, you can unlock its full potential and harness it to drive meaningful change. Whether you are a designer, a business leader, or an individual seeking to solve complex problems, design thinking can provide you with a powerful framework to approach challenges in a creative and empathetic way.
Using brainstorming to generate innovative ideas
In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, generating innovative ideas is crucial for businesses to stay ahead of the curve. One effective method to generate ideas and foster creativity is through brainstorming. Brainstorming is a collaborative technique that allows individuals or teams to come together and generate a wide range of ideas without any constraints or judgment. It encourages participants to think outside the box and push the boundaries of conventional thinking.
When conducting a brainstorming session, it is essential to create a conducive environment where every idea is given equal importance. By encouraging all participants to contribute their thoughts and ideas, a wide variety of perspectives are brought to the table. This diversity helps in expanding the possibilities and exploring uncharted territories.
During a brainstorming session, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure its effectiveness. Firstly, participants should be encouraged to think freely and avoid self-censorship. All ideas, no matter how wild or unconventional, should be welcomed and noted down. This encourages a non-judgmental atmosphere where everyone feels comfortable sharing their thoughts.
- Quantity over quality: The goal of brainstorming is to generate a large quantity of ideas. It is important to emphasize that the focus at this stage is on quantity rather than quality. The more ideas generated, the better the chances of finding innovative and unique solutions.
- Build upon ideas: Participants should be encouraged to build upon the ideas shared by others. This helps in developing concepts further and exploring different possibilities. By leveraging the collective intelligence of the group, ideas can be refined and transformed into groundbreaking innovations.
- Time constraints: Setting a time limit for brainstorming sessions can help in maintaining focus and driving productivity. By setting a specific duration, participants are encouraged to think quickly and avoid overthinking. This helps in capturing spontaneous and fresh ideas.
After the brainstorming session, the ideas generated need to be organized and evaluated. This can be done through various methods, such as grouping similar ideas together or prioritizing them based on their feasibility and potential impact. Once the ideas are organized, they can be further refined and developed through other design thinking techniques like prototyping and user feedback.
| Benefits of brainstorming | Challenges of brainstorming |
|---|---|
|
|
In conclusion, brainstorming is a powerful technique to generate innovative ideas. By providing a platform for collaboration, creativity, and open-mindedness, brainstorming allows businesses to tap into the collective wisdom of their teams and come up with groundbreaking solutions. When implemented effectively, brainstorming can be a catalyst for driving innovation and staying ahead in today’s competitive landscape.
Empathy mapping to understand user needs
Empathy mapping is a powerful tool used in design thinking to understand the needs and desires of users. By putting ourselves in the shoes of the users, we can gain deep insights into their emotions, behaviors, and motivations. This enables us to design products and services that truly resonate with the target audience.
The process of empathy mapping involves creating a visual representation of the user’s experience, thoughts, and feelings. It helps us to go beyond assumptions and stereotypes, and develop a deeper understanding of the user’s perspective. The goal is to identify their pain points, aspirations, and motivations, and use this information to develop innovative solutions.
To create an empathy map, a team of designers and stakeholders gather together and brainstorm their understanding of the user. This can be done by asking questions such as: What does the user see? What do they hear? What do they say and do? What are their pain points and challenges? What are their goals and aspirations? The answers to these questions are then categorized into four sections: thinking, feeling, saying, and doing.
Once the empathy map is complete, it provides a comprehensive overview of the user’s needs and desires. It helps the design team to identify opportunities for improvement, and develop solutions that address these needs. The empathy map can also be used as a communication tool to share insights with other stakeholders and team members.
Using empathy mapping in design thinking is a powerful approach to understand user needs. It helps designers to develop products and services that meet the desires and aspirations of the target audience. By putting empathy at the heart of the design process, we can create solutions that truly make a difference in people’s lives.
Prototyping to visualize and test ideas
Prototyping is a crucial step in the design thinking process. It allows designers to visualize and test their ideas before implementing them fully. A prototype is a simplified version of a product or service that captures the essence of the idea. It provides a tangible representation of the concept, helping designers identify potential flaws and refine their design. Through prototyping, designers can gather valuable user feedback and make necessary improvements.
There are various types of prototypes that can be used, depending on the stage of the design process and the desired outcome. Low-fidelity prototypes, such as sketches or cardboard models, are quick and inexpensive to create. They are useful for early-stage concept testing and brainstorming. On the other hand, high-fidelity prototypes, such as interactive digital models or 3D-printed mock-ups, provide a more realistic representation of the final product. These prototypes are ideal for user testing and validation.
Prototyping not only helps designers validate their ideas but also encourages collaboration and communication within the design team. By having a tangible model to refer to, team members can easily discuss and suggest improvements. It allows for a shared understanding of the design and enables designers to gather diverse perspectives. The iterative nature of prototyping also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, as each iteration builds upon the previous one.
In addition to enhancing communication within the design team, prototyping also aids in effectively communicating ideas to stakeholders and clients. Instead of relying solely on verbal explanations or static drawings, a prototype provides a hands-on experience. It allows stakeholders to interact with the design concept, providing them a better understanding of its functionality and potential. This interactive experience can greatly influence decision-making and facilitate buy-in from stakeholders.
- Prototyping helps visualize and test ideas before implementation.
- There are various types of prototypes for different stages of the design process.
- Prototyping encourages collaboration and communication within the design team.
- It aids in effectively communicating ideas to stakeholders and clients.
- Prototyping enables gathering user feedback and making necessary improvements.
| Benefits of Prototyping |
|---|
| 1. Visualizes ideas |
| 2. Tests usability and functionality |
| 3. Enables collaboration within the design team |
| 4. Facilitates communication with stakeholders and clients |
| 5. Supports iterative design and continuous improvement |
Iterative design process for continuous improvement
The iterative design process is a crucial component of design thinking, allowing for continuous improvement and refinement of ideas. By consistently reviewing and testing design solutions, teams can gather valuable feedback and make necessary adjustments. This process emphasizes the importance of learning from failures and using them as opportunities for growth.
One of the key aspects of the iterative design process is the emphasis on feedback. Throughout each stage of the design process, it is essential to gather feedback from users, stakeholders, and team members. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that the final solution meets user needs and expectations. By incorporating feedback early and often, teams can save time and resources by addressing issues before they become more significant problems.
Another important aspect of the iterative design process is prototyping. Prototyping allows teams to visualize and test their ideas before committing to a final design. By creating prototypes, teams can gather feedback early on and make necessary adjustments. This not only saves time but also allows for more creative exploration and innovation. Prototyping can take many forms, from low-fidelity sketches and wireframes to high-fidelity interactive prototypes.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Define | During this stage, teams identify the problem they are trying to solve and gather insights from users and stakeholders. They define the project scope and set goals for the design process. |
| Ideate | In this stage, teams generate a wide range of ideas and potential solutions. Brainstorming sessions and other ideation techniques are used to encourage creativity and innovative thinking. |
| Prototype | Teams develop prototypes to bring their ideas to life. Prototyping can involve creating physical models, digital mockups, or interactive prototypes, depending on the nature of the project. |
| Test | During the testing stage, teams gather feedback from users and stakeholders through usability tests and other methods. This feedback helps identify areas for improvement and informs further iterations. |
| Refine | Based on the feedback received during testing, teams refine their designs and make necessary adjustments. This process is repeated multiple times until the final design is ready to be implemented. |
In conclusion, the iterative design process is an integral part of design thinking, enabling teams to continuously improve their solutions. By embracing feedback, prototyping, and collaboration, teams can create user-centered designs that address complex problems effectively. This approach encourages a culture of learning and innovation, paving the way for exceptional design outcomes.
Collaborative teamwork in design thinking workshops
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and collaboration. It involves a series of steps that help teams develop innovative solutions to complex problems. One crucial aspect of design thinking is collaborative teamwork. In design thinking workshops, individuals from diverse backgrounds come together to share their unique perspectives and collectively brainstorm ideas. This collaboration fosters a creative and inclusive environment that allows for the generation of innovative ideas.
Collaborative teamwork in design thinking workshops allows participants to pool their knowledge and expertise, leading to a holistic understanding of the problem at hand. By working together, team members can explore various angles and uncover hidden insights. This approach encourages active participation and engagement from all team members, ensuring that multiple perspectives are considered during the ideation process.
In a design thinking workshop, it is important to create a safe and supportive space where individuals feel comfortable expressing their ideas. This can be achieved through effective facilitation techniques, such as active listening, encouraging equal participation, and valuing diverse opinions. By fostering a collaborative environment, teams can leverage the collective intelligence of the group and build on each other’s ideas to create innovative solutions.
- A collaborative approach encourages open-mindedness and allows individuals to learn from one another.
- Teams can benefit from the diverse range of skills and expertise present in the workshop.
- Collaboration helps in challenging assumptions and encourages outside-the-box thinking.
| Benefits of Collaborative Teamwork in Design Thinking Workshops |
|---|
| 1. Enhanced creativity and innovation |
| 2. Increased problem-solving capabilities |
| 3. Improved decision-making through collective input |
| 4. Strengthened team dynamics and cohesion |
| 5. Greater empathy and understanding of user needs |
In conclusion, collaborative teamwork plays a vital role in design thinking workshops. By leveraging the diverse perspectives and skills of team members, it fosters a creative and inclusive environment where innovative ideas can flourish. Effective collaboration allows for a holistic understanding of the problem and the development of solutions that address the needs of users. Through collaborative teamwork, design thinking workshops can empower teams to solve complex problems and drive meaningful innovation.
Applying design thinking to solve complex problems
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that focuses on the needs of the end user. It is a method that can be applied to solve a wide range of complex problems, from product design to business strategy. By using a combination of empathy, creativity, and iterative testing, design thinking enables teams to come up with innovative solutions that truly meet the needs of their target audience.
One of the key principles of design thinking is understanding the problem. This involves conducting research, gathering data, and empathizing with the end user to gain a deep understanding of their needs and pain points. By putting yourself in the user’s shoes and experiencing their challenges firsthand, you can develop a deep empathy for their situation. This empathy helps guide the design process and ensures that the solutions you create are truly valuable and meaningful.
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, the next step in applying design thinking is brainstorming. Brainstorming involves generating a large number of ideas and solutions in a short period of time. This is a critical step in the design thinking process, as it allows the team to explore a wide range of possibilities and think outside the box. By encouraging open and non-judgmental discussion, brainstorming can lead to innovative ideas that may not have been considered otherwise.
After generating a list of potential solutions, the next step is to prototype and test these ideas. Prototyping involves creating a physical or digital representation of the solution in order to gather feedback and test its effectiveness. This can range from creating a simple paper prototype to developing a fully functional prototype. By testing the solution with real users, you can gather valuable insights and make iterative improvements based on their feedback.
The design thinking process is inherently iterative, meaning that it involves continuous improvement and refinement. After testing and gathering feedback on a prototype, the team can use this information to make further iterations and improvements. This iterative process allows for constant learning and adaptation, ensuring that the final solution is as effective and user-friendly as possible.
Collaborative teamwork is another important aspect of applying design thinking to solve complex problems. Design thinking encourages multidisciplinary teams to work together, combining their unique perspectives and expertise to come up with innovative solutions. By fostering a collaborative and inclusive environment, design thinking enables teams to leverage the collective intelligence and creativity of all team members.
In conclusion, applying design thinking to solve complex problems is a powerful approach that can lead to innovative and user-centered solutions. By understanding the problem, brainstorming ideas, prototyping and testing, and embracing an iterative and collaborative mindset, teams can tackle even the most complex challenges and create meaningful impact. So, next time you face a complex problem, consider applying design thinking principles to unlock new possibilities and drive innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the principles of design thinking?
The principles of design thinking include empathy, collaboration, experimentation, and iteration. These principles guide the design process and help create innovative solutions.
2. How does brainstorming help generate innovative ideas?
Brainstorming is a collaborative technique that encourages free thinking and idea generation. By allowing individuals to express their thoughts and build upon each other’s ideas, brainstorming helps generate a wide range of innovative solutions.
3. What is empathy mapping and why is it important in design thinking?
Empathy mapping is a tool used to understand the needs, wants, and motivations of users. It helps designers gain a deeper understanding of user perspectives and allows them to design solutions that meet those needs effectively.
4. How does prototyping contribute to the design process?
Prototyping involves creating a visual or tangible representation of an idea. It allows designers to test concepts and gather feedback before investing time and resources into the final solution. Prototyping helps in refining and improving ideas based on user feedback.
5. What is the iterative design process and why is it important?
The iterative design process involves continuously refining and improving a design based on feedback and testing. It helps in uncovering better solutions, enhancing the user experience, and increasing the overall effectiveness of the design.
6. How does collaborative teamwork impact design thinking workshops?
Collaborative teamwork encourages diverse perspectives and fosters creativity in design thinking workshops. It allows for the exchange of ideas, promotes innovation, and ensures that the best ideas are incorporated into the final design solution.
7. How can design thinking be applied to solve complex problems?
Design thinking provides a structured approach to solving complex problems by focusing on understanding user needs, generating innovative ideas, prototyping and testing solutions, and iterating based on feedback. This systematic approach helps break down complex problems into manageable steps to arrive at effective solutions.